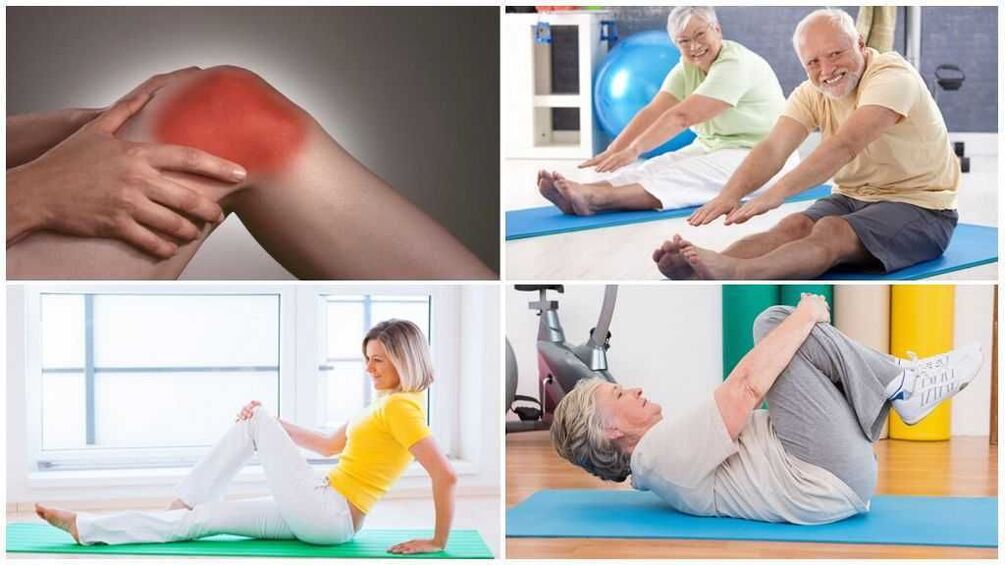
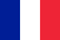
Arthropathy: Degree and Type of Disease
degree of joint disease
- first level– At this stage of the disease, patients may experience only mild pain in their joints after engaging in physical activity or remaining in one position for an extended period of time. Noise may also be lost when moving the joint.
- second degree– During this stage of arthrosis, the pain becomes more severe, especially when moving, and the bones within the joint may also swell and shift.
- Three degrees– The most severe stage of arthrosis, when the pain syndrome becomes unbearable and the joints are unable to fully perform their functions. In this case, immediate medical attention is required.
Types of Arthropathy
- knee joint disease- This is one of the most common types of arthropathy affecting the knee joint. It can be caused by joint injury or overuse as well as genetic factors.
- hip jointIt is a disorder of the pelvis and hip joints that often occurs in people over 50 years of age or those who are predisposed to the disease.
- elbow jointis a disease that affects the elbow joint. It usually occurs due to injury or overuse of the joint, as well as repeated minor injuries that cause microtrauma to the joint.
- shoulder jointis a disorder of the shoulder joint that can occur due to injury or various diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis or juvenile arthritis.
Arthropathy: Concept and Developmental Causes
The main cause of arthrosis is damage to the cartilage responsible for the shock-absorbing function of the joints. Injuries may be caused by mechanical damage, increased load on certain areas, impairment of blood circulation and tissue nutrition.
- coxarthrosis (hip joint injury);
- Styroarthrosis (knee joint injury);
- humerus arthrosis (shoulder joint injury);
- Radiocarpal arthropathy (injury to the radiocarpal joint);
- Interphalangeal joint disease (injury to the interphalangeal joints of the fingers).
Types of Arthropathy
Osteoarthritis
Post-traumatic arthropathy
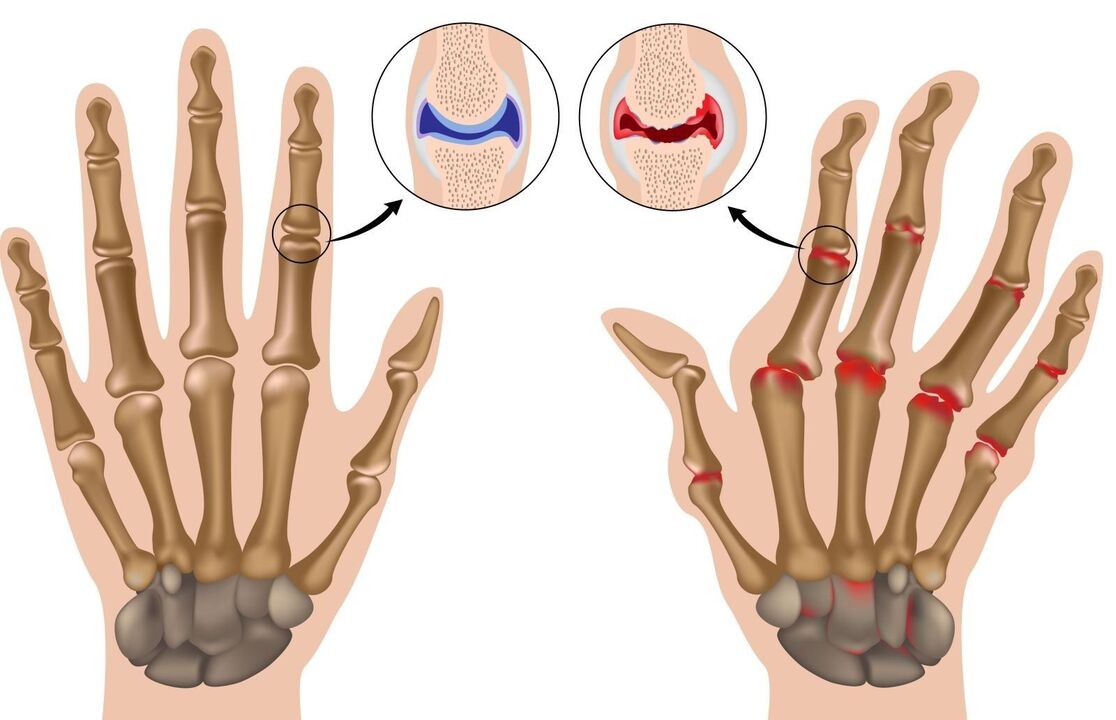
rheumatoid arthritis
How do joints develop?
When cartilage begins to wear away, its mechanical shock-absorbing function is compromised and pathological contact between joint segments develops. The worn bone limbs become rough and jagged and protrude from the flat surfaces of the joints. This leads to a breakdown in the adhesion of the joint surfaces to each other, increasing the load on the joint surfaces and creating additional friction, which accelerates the wear and tear of the cartilage.
Arthropathy: Types, Degrees, Symptoms
What are the symptoms of arthritis?
- joint pain. This is the most common symptom of joint disease. Typically, pain increases with movement and decreases with rest. It may be sharp or dull.
- Limited joint movement. When you have arthrosis, you may feel like your joints become stiff and unable to move. For example, patients may have difficulty bending or straightening their knees or elbows.
- Creaking or noise when moving. With arthrosis, the joints may make a crunching or noise every time you move.
- swelling and redness. In some cases of joint disease, it can cause swelling and redness in the joints. However, this rarely happens.
- joint deformity. As the disease progresses, chronic deformation of the joints may occur, accompanied by pain and limited mobility.
How is arthritis diagnosed?
Basic diagnostic methods
- clinical examination of the patient;
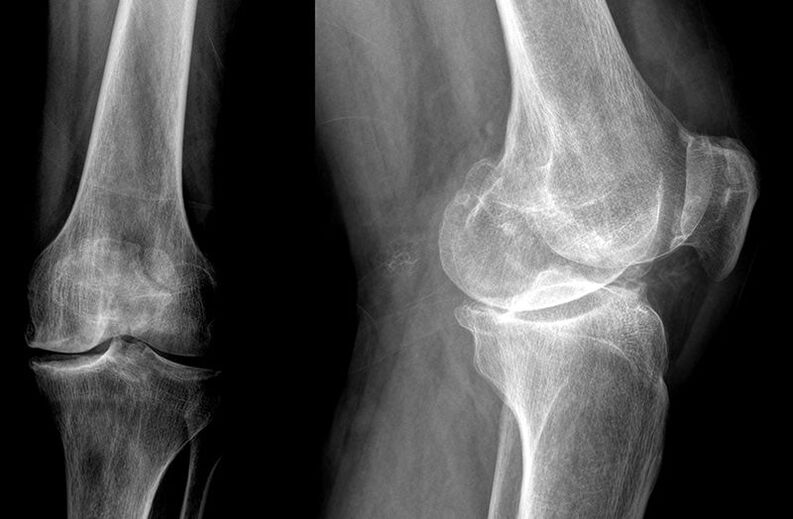
- radiography;
- magnetic resonance imaging (MRI);
- Computed tomography (CT);
- Arthroscopy.
clinical examination
radiography
Magnetic resonance imaging
CT scan
Arthroscopy
Treatment of arthropathy: characteristics depend on the degree of development
1st degree arthropathy
2nd degree arthropathy
third degree arthropathy
Basic methods to prevent joint disease
maintain a normal weight
exercise regularly
Choose the right shoes
nutritious food
Observe hygiene rules and prevent joint injuries
Complications of Arthropathy
Other complications of arthropathy include limited joint movement and loss of function. In some cases, surgery may be needed to correct the problem.
Arthropathy and Disability: What Do You Need to Know?
What is joint disease?
Type and degree of joint disease
joints and disabilities
Arthropathy and Disability Limitations
How can you keep your joints healthy if you have arthritis?
maintain a normal weight
engage in physical activity