What is osteochondrosis?
refer to.Most often, spinal osteochondrosis is diagnosed in people over 25 years of age. According to statistics from the World Health Organization, as of 2021, 43% of the population aged 25-40 suffers from osteochondrosis, and more than 92% of them are elderly. The appearance and exacerbation of the disease can be caused by surrounding adverse factors.
Types of osteochondrosis
- Lumbar osteochondrosis.The lower back consists of 5 vertebrae, which are susceptible to deformation due to the negative influence of external and internal factors. When the nutritional and metabolic processes in the intervertebral disc are disrupted, pain occurs as the cartilage tissue loses elasticity and becomes thinner.
- Cervical osteochondrosis.The cervical spine is made up of 7 vertebrae and is constantly under pressure. When the body's metabolic processes fail, pathological processes are activated.
- Osteochondrosis of the chest.The thoracic area is made up of 12 vertebrae. This type of osteochondrosis is the least common. The thoracic spine is immobile. People who lead a passive lifestyle and frequently lift heavy objects are susceptible to this disease.
Causes of osteochondrosis
important!With age/due to heavy loading, the discs and cartilage can deform. Fissures and hernias may occur. As a result, nerve roots become compressed, intervertebral discs become thinner, pathological processes occur in the spinal cord, muscle spasms and progressive pain occur.
- Have a family history of osteochondrosis;
- Overweight, obesity;
- passive lifestyle;
- flatfoot.
- Self-neglect (complete lack of physical activity or excessive exercise).
- Lack of awareness of proper posture to reduce stress on the spine.
- Continuous work involving lifting/moving heavy objects.
- Injuried.
Osteochondrosis: 4 stages of disease development
- The first stage– There are no clear symptoms to diagnose the disease. Back pain occurs occasionally, usually after physical exertion or overexertion. Early osteochondrosis can be detected during preventive exams or during CT or X-ray examinations.
- second stage.The next stage is characterized by moderate pain. The cartilage tissue begins to deform, and the distance between the discs decreases. When a doctor is contacted, he or she will prescribe medication (to relieve pain) and physical therapy.
- The third phase– Deformation of the spine, fibrous areas and hernias appear, pain intensifies, becomes more pronounced and frequent. At this stage, everything depends on the existing symptoms. The doctor will help determine the patient's treatment (conservative or surgical).
- Stage 4– Irreversible deformation of spinal function. It is almost impossible for the patient to move independently. The pain is severe, constant, and worsens with any physical activity. Pathological bone tissue fills the intervertebral spaces and the patient becomes disabled.
Symptoms of osteochondrosis
Symptoms of lumbar osteochondrosis
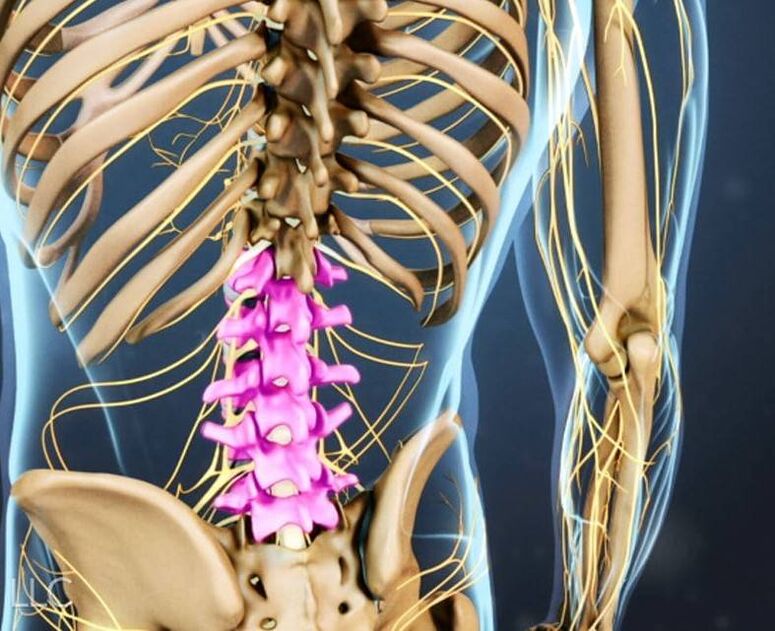
- Stiff movements;
- Pain in the pelvis, sacrum, lower back, and lower extremities that becomes more severe with exercise or movement. The nature of the pain is aching, dull, sharp;
- Pathological processes of the genitourinary system (problems with defecation and urination);
- Weakness in the legs;
- Impairment/lack of sensitivity.
important!Self-medication is strictly prohibited. When lumbar osteochondrosis is discovered, diagnosis and effective treatment are necessary. The consequences of lack of treatment are hernias, herniations, and paralysis of the lower limbs.
Symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis
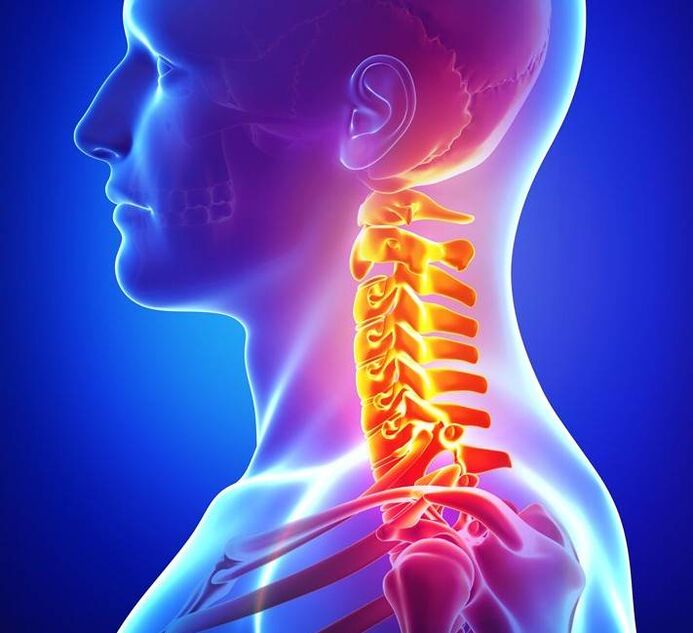
- Frequent headaches;
- numbness in upper and lower limbs;
- Severe creaking of the cervical spine during physical activity;
- "Spots", spots in the eyes, clouding and darkening;
- Burning and discomfort in the heart area;
- Tinnitus and hearing loss occur;
- Unexplained dizziness;
- Shoulder, neck, arm pain.
important!Cervical osteochondrosis is considered one of the most dangerous diseases for humans because it complicates the process of filling the brain with blood. If left untreated, a protrusion will develop and then a hernia will develop. Surgical intervention for cervical osteochondrosis carries a high risk of physical paralysis. If symptoms occur, please contact only a qualified specialist.
Symptoms of thoracic osteochondrosis
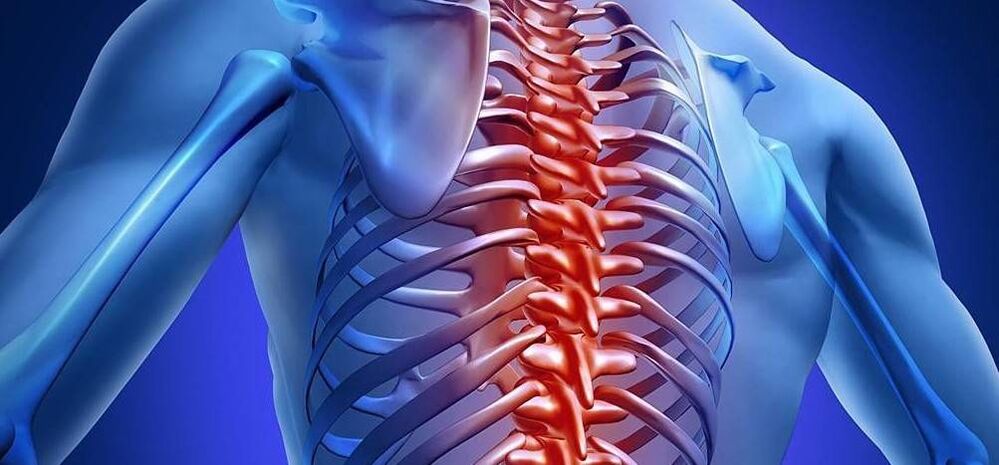
- Discomfort, burning sensation in the chest area;
- Pain when raising arm, pain in shoulder blade;
- Dizziness and sudden loss of consciousness;
- Chest pain.
refer to.During the transition to the acute phase of the disease, back pain (lack of air, sharp/stiff chest pain, "lumbar pain") and back pain (pain can be paroxysmal or persistent, acute/dull in nature) may occur).
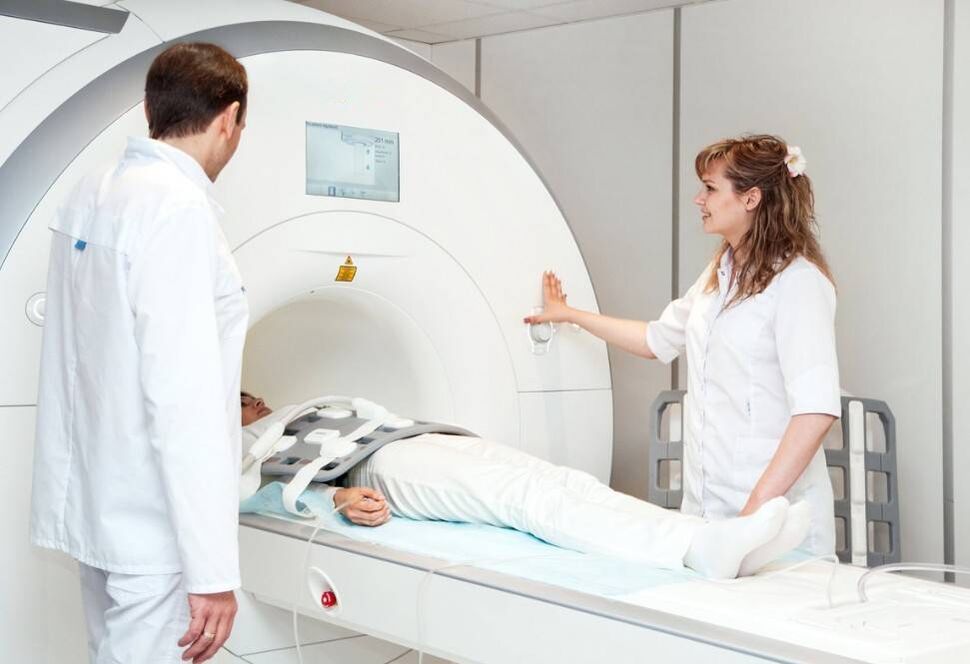
Diagnosis of spinal osteochondrosis
Patient equipment. The specialist will check the integrity of the reflexes and the sensitivity of the painful area. Blood tests and other laboratory tests are then performed. To confirm the diagnosis, a neurologist will order one or more types of diagnostic imaging:
- Vertebral artery ultrasonography.
- X-rays of the entire spine or certain areas (cervical, thoracic, lumbar).
- A CT scan of the spine helps identify the presence of degenerative processes, displacements, deformations of the spine and its structures.
- Spine MRI - identifies soft tissue lesions and helps scan the spinal cord and intervertebral discs.
Treatment of osteochondrosis
Drug treatment of osteochondrosis
- NSAIDs (Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs) – Relieve symptoms of osteochondrosis, relieve pain, reduce inflammation. Available in tablet form or as an injection (in severe cases). Treatment courses last 7 to 14 days;
- Chondroprotectant – strengthens intervertebral discs and cartilage tissue;
- B vitamins;
- Vascular medications – improve blood supply to the spine;
- Glucocorticoids – injections into the affected area (for severe disease);
- Muscle Relaxants – Relax muscles and relieve pain and inflammation.
Massage treatment for osteochondrosis
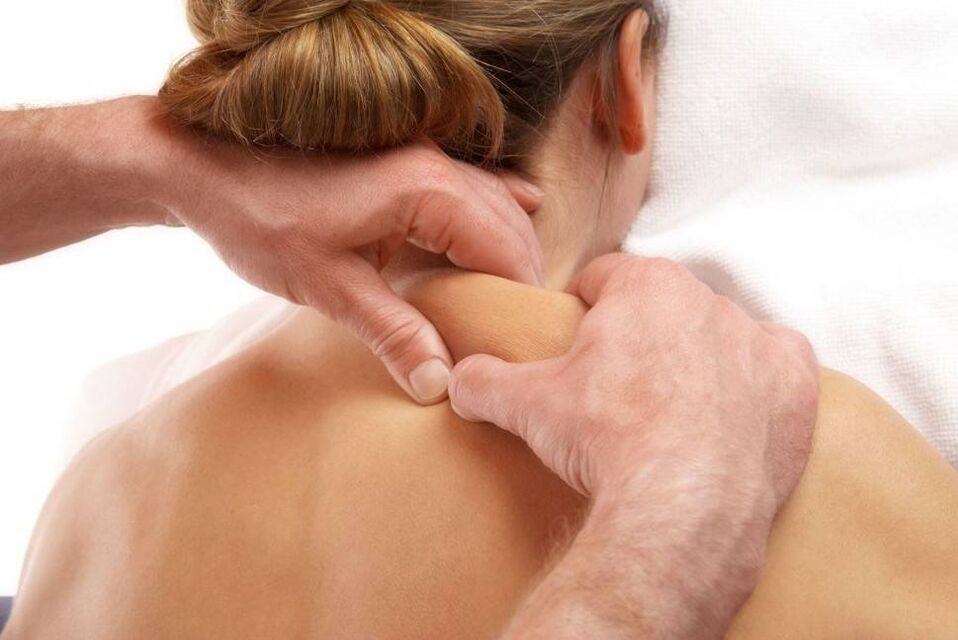
Traction (spinal traction)
manual therapy
Physical therapy for osteochondrosis
acupuncture

Exercise therapy for osteochondrosis
important!During exacerbation of osteochondrosis, exercise therapy sessions are contraindicated!
Surgical treatment of osteochondrosis
Prevention of spinal osteochondrosis
- Place your forehead on your palms and tense your neck muscles. Execution – 3 sets of 5-7 seconds each. Then repeat the same action on the back of your head and palms.
- The position of the shoulders is level and the head is straight. Slowly tilt your head as far to the right and then to the left. Executed 5 times (slowly).
- Slowly tilt your head back a little. Tighten your neck muscles and gradually move your chin toward your chest. Do 5-7 times.
- Place your left palm near your left temporal area (then your right palm and right temple). Apply pressure to your palms and tense your neck muscles. Execute - 3 times for 10 seconds.
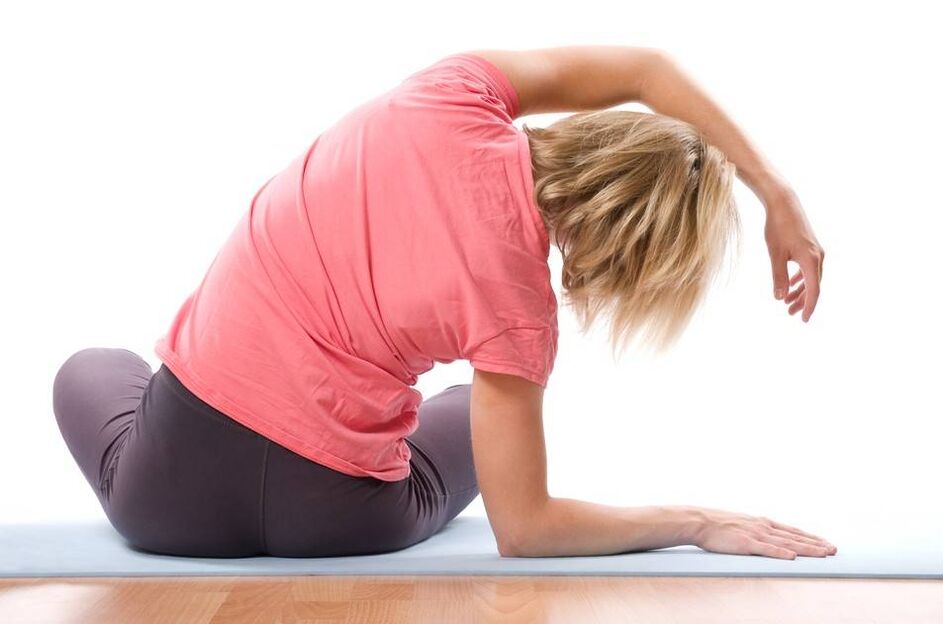

important!Don't rush when practicing. Circular head movements are also prohibited due to the high risk of injury and pinched nerve endings.
- Stand up straight, feet together, arms relaxed, and take a deep breath. Raise your arms and exhale. Close – 6-8 times.
- Lie on your stomach with your arms resting on your body and relax. Bend upwards, rest your hands, and try to lift your head and feet. Hold this position for 5 seconds. Return to starting position. Repeat – 5-7 times.
- sit on the chair. Place your hands behind your head (take a deep breath) and bend back 4-5 times so that your shoulder blades touch the back of the chair (exhale). Repeat – 5-7 times.
- Stand up, bend back, and take a deep breath. Relax your arms, lean forward, and slowly lower your head and shoulders—exhale. Close - 10 times.
- Get on all fours. Head straight. Arch your back and hold this position for 3-4 seconds. Return to starting position and repeat 5-7 times.
How to stand, lie down and sit with osteochondrosis?
How to sit correctly?
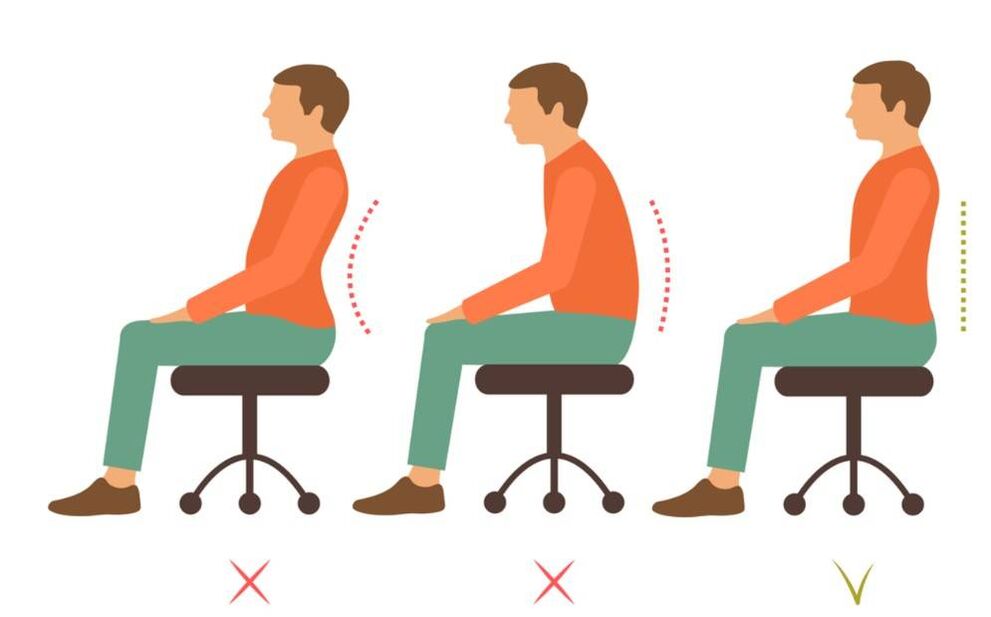
- Criteria for choosing a chair / chair: Seat depth level - 2/3 of the hip length, seat height level should be equal to the length of the calf. This way your feet will be on the floor. Short people will need a small step or stool under their feet;
- Pay attention to the depth of the tabletop. The legs do not have to be placed to the side or strongly bent;
- When sitting for long periods of time at work, take breaks every 20 minutes. Change the position of your legs, walk around, do light exercises;
- Sit behind the wheel with minimal stress. Your back should be resting against the seat; placing a small pillow or cushion between the chair and your lower back can help. If possible, get out of the car and warm up every 25-30 minutes;
- Heavy, upholstered furniture is not suitable for everyday use. In order for the spine to bear an even load, the body needs to be supported by the ischial tuberosities, which is only possible while sitting on a moderately hard surface;
- Your back should always be in contact with the backrest of the chair/task chair. Sit up as straight as possible and avoid sharp bends in your neck;
- Do not sit/lie in one position for long periods of time.
How to stand correctly?
- Do not stand in one position for more than 10 minutes and change the position of your legs and arms;
- Relieve neck tension - tilt your head from side to side, extend your arms forward, bend your back forward and backward - relax your back and lower back;
- Find support for your hands when lifting items from the floor, stooping, bending your knees, or squatting;
- Move, walk short distances to avoid standing still;
- Try not to bend (back, head) too much when doing housework (cleaning, ironing, cooking). Get down on one knee when cleaning low or hard-to-reach surfaces.
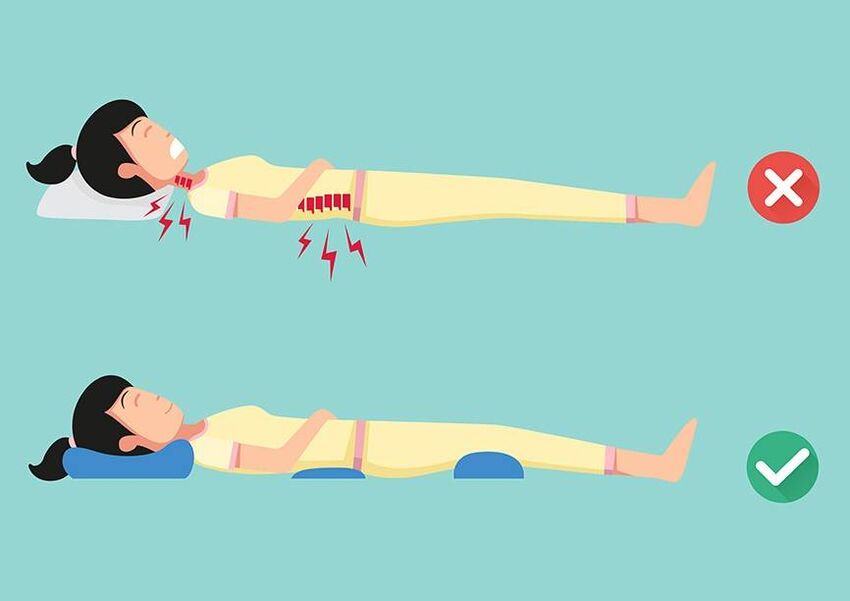
How to lie down?
- Back pain - lie on your stomach with a small pillow under your waist (so as not to aggravate pain when bending over);
- Leg pain - place a pad (towel or blanket) under your knees. The pain syndrome will gradually lessen;
- Neck pain - Place your hands under your head or place a pad under your neck.
- Conduct a brief warm-up of upper and lower limbs;
- change your stance;
- From a lying position to a sitting position, bend your hands at the knees and hug your legs;
- Lower your legs one by one to the floor;
- Get up gradually, any sudden movement will increase the pain.
How to properly lift and move heavy objects?
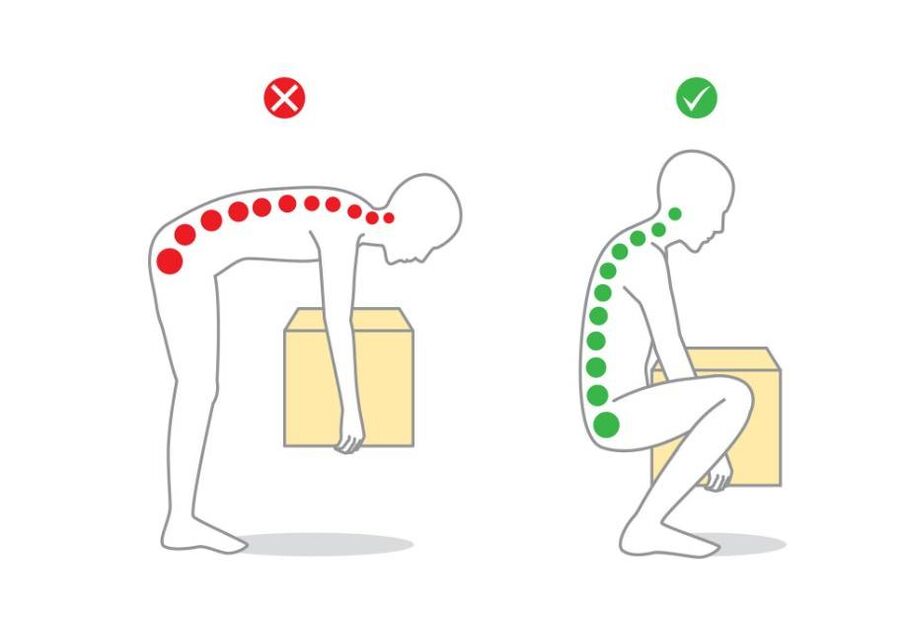
- Wear a wide belt.
- Squat down. Keep your neck and back straight.
- Use your hands to hold the object in place and slowly stand up, keeping your back straight.
- Distribute the load evenly between your hands and don't carry everything with one hand;
- After diagnosis of osteochondrosis, it is not recommended to lift more than 15 kilograms;
- Buy a backpack (an important condition is an orthopedic back and wide shoulder straps). The advantage of using a backpack is that the spine is evenly loaded + hands free;
- Do not lean forward or backward sharply.